Wireguard VPN erstellen
Ganz einfach Möglichkeit ist es, das VPN als PiVPN zu installieren
Installation
curl -L https://install.pivpn.io | bashYes, that's it! It is *almost* that simple.
To elaborate a little more, you will want to install Raspberry Pi OS Lite on a Raspberry pi, we strongly recommend using the latest Raspberry Pi OS Lite image but the normal Raspberry Pi OS image will work as well, preferably enable ssh access and then begin.
After install, you may need to open a port on your router.
There is a (now slightly outdated) guided walkthrough of the install available here.
More information is also available on the PiVPN GitHub
Konfiguration eines Clients
Generating Private and Public Keys
WireGuard works by encrypting the connection using a pair of cryptographic keys. The key pair is used by passing the public key to the other party, which can then encrypt its message so that it can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key. To secure two-way communication, each side must have its own private and public keys, since each pair provides only one-way messaging.
Generate a client public and private key pair by running the following command:
pivpn -add
die public keys befinden sich im Ordner /home/pivpn/config
After that, create a client configuration file, in the following directory:
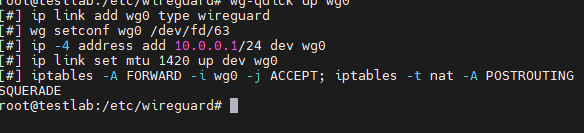
sudo nano /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
In the file type:
[Interface]
PrivateKey = <contents-of-client-privatekey>
Address = 10.0.0.1/24
PostUp = iptables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
PostDown = iptables -D FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
ListenPort = 51820
[Peer]
PublicKey = <contents-of-server-publickey>
AllowedIPs = 10.0.0.2/32Notes: In the publickey line insert the server public key that we generated in the previous article and on the private key insert the client private key.
WireGuard Startup
To start the connection, type the following command:
sudo wg-quick up wg0
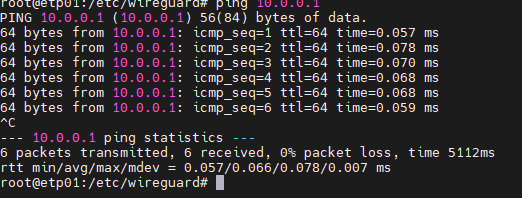
Now the client can communicate with the server, you can ping the server from the client with the command
ping 10.0.0.1
To find out the connection status, run the following command:
sudo wg show
You will get all the connection details as shown below
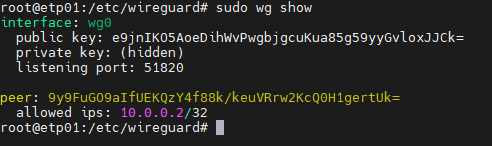
Congratulations! Your client computer now has access to the VPN network.
Der folgende Abschnitt zeigt die Konfiguration eines WireGuard Clients unter Ubuntu 20.04 und 18.04.2 LTS.
WireGuard Private- und Public-Key für den Ubuntu Rechner erzeugen
Für eine erfolgreiche Verbindung benötigt jeder Teilnehmer an einem WireGuard VPN eigene Private- und Public-Keys. Sie können diese bequem mit dem nachfolgenden Befehl erzeugen. Die umask wird auf 077 gesetzt, um alle anderen User außer root den Zugriff zu verweigern.
$ sudo -i
# cd /etc/wireguard
# umask 077
# wg genkey > private-key
# wg pubkey > public-key < private-key
Dauerhafte Konfiguration anlegen
Wie Sie eine dauerhafte, auch einen Neustart überstehende, Konfiguration erzeugen wird in diesem Abschnitt beschrieben.
Erstellen Sie dazu beispielsweise mit dem Editor vim die neue Datei wg0.conf:
$ sudo vi /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
Fügen Sie nun in diese Datei die folgenden Zeilen ein. Speichern und verlassen des vim können Sie anschließend mittels :x. Für ein besseres Verständnis sind die einzelnen Zeilen per Inline-Kommentar beschrieben.
# Beispiel
[Interface]
Address = <Konfigurierte Client IP>/<Netmask> // Zum Beispiel die IP "10.11.0.20/32"
PrivateKey = <Private Key des Clients>
[Peer]
PublicKey = <Public Key der OPNsense Wireguard Instanz>
AllowedIPs = <Netzwerke auf die dieser Client Zugriff haben soll>/<Netmask>
// Zum Beispiel "10.11.0.0/24, 192.168.1.0/24"
// | |
// +--> der Netzwerkbereich des OPNsense WireGuard VPNs
// |
// +--> Netzwerk hinter der Firewall
Endpoint = <Public IP der OPNsense Firewall>:<WireGuard Port>
config proxi
[Interface]
Address = 10.213.114.4/24
PrivateKey = 0De/ERM5Z1fWjhRpgXldts7IKUmj2RaNmjIY+2ACMVA=
[Peer]
PublicKey = BItDBtfCVugVED9BHc6vG66Lh+3iyWPf73HGJPSosxs=
PresharedKey = r6pcrvFiSoTTclHMoZDsn4PqTn0ghdt/OT+UTXgdQoY=
Endpoint = hhml.selfhost.co:51821
AllowedIPs = 0.0.0.0/0, ::0/0
Systemd Service anlegen
Das WireGuard VPN kann über einen Systemd Service gesteuert werden, damit beim Starten von Ubuntu das VPN automatisch aufgebaut wird.
$ sudo systemctl enable wg-quick@wg0.service
Kommandos zur Steuerung des Systemd Services:
$ sudo systemctl start wg-quick@wg0.service
$ sudo systemctl status wg-quick@wg0.service
$ sudo systemctl stop wg-quick@wg0.service